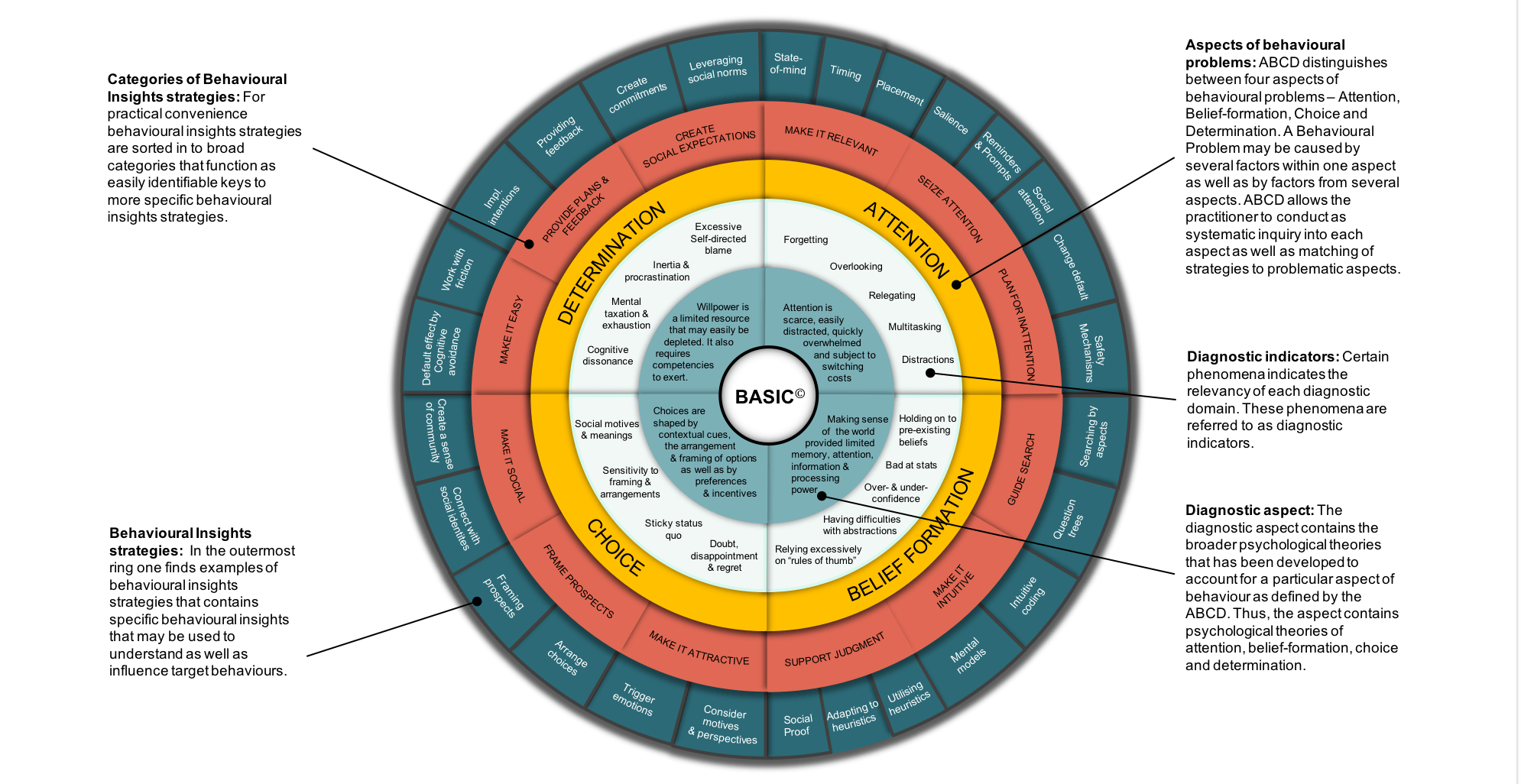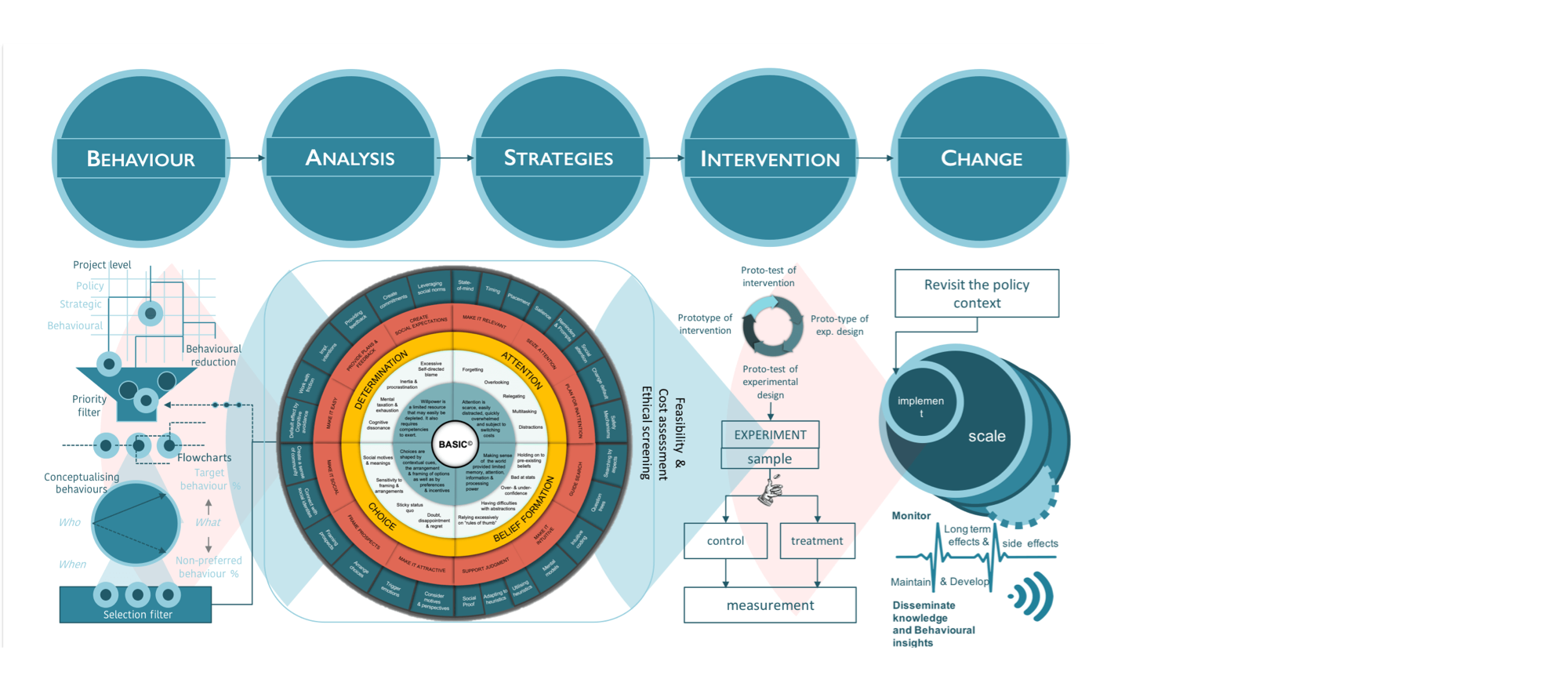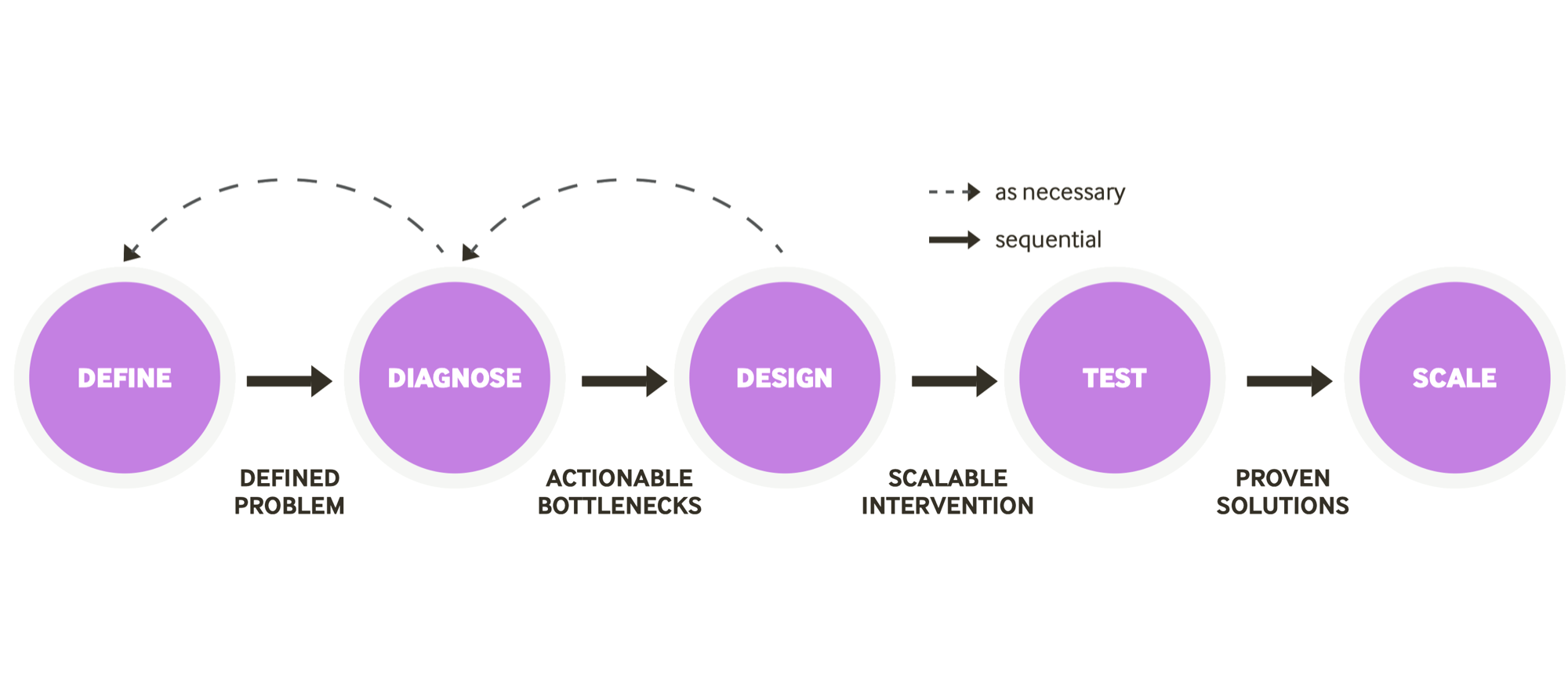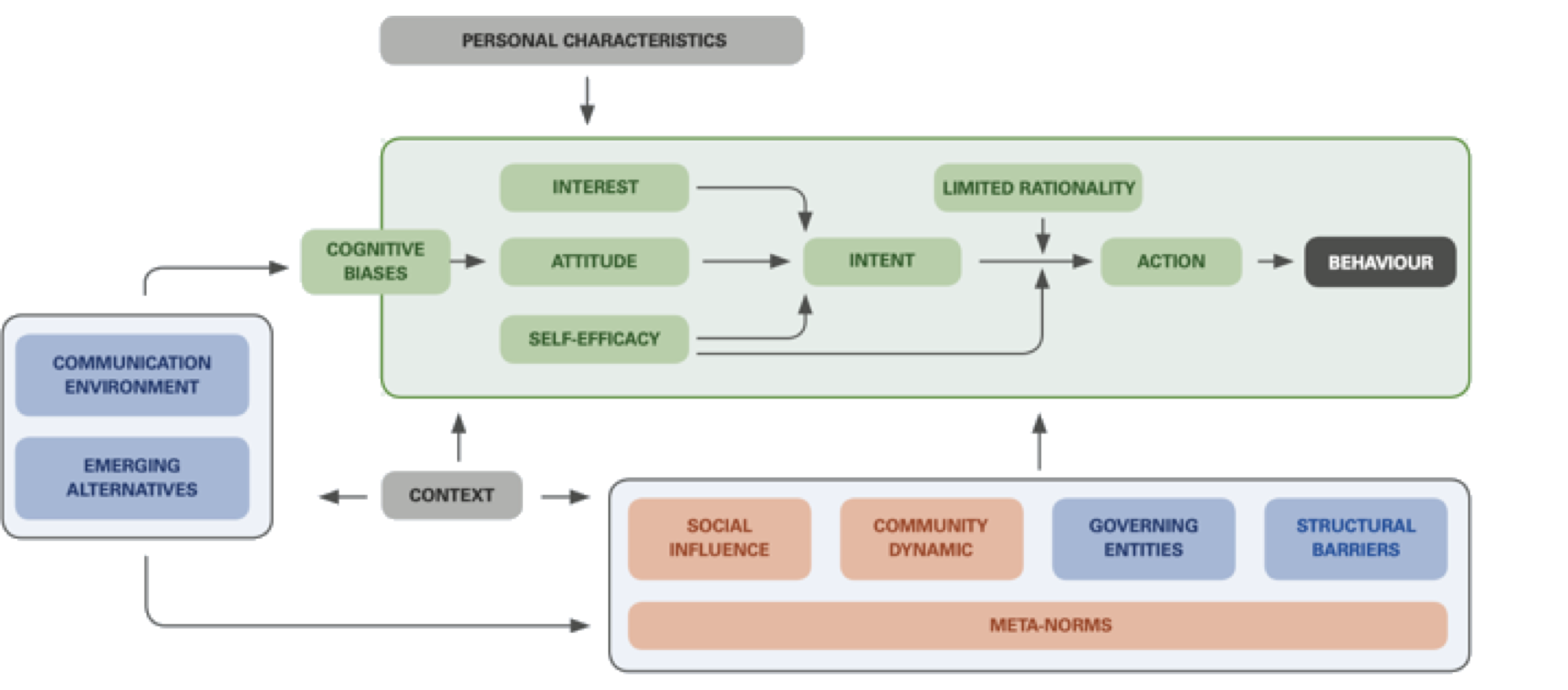
Health Action Process Approach(HAPA)
Behavior Model • 1992
Ralf Schwarzer
The Health Action Process Approach (HAPA) is a framework for health behavior change and intervention design.
HAPA combines elements of Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory (SCT), the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), and the Transtheoretical Model (TTM).
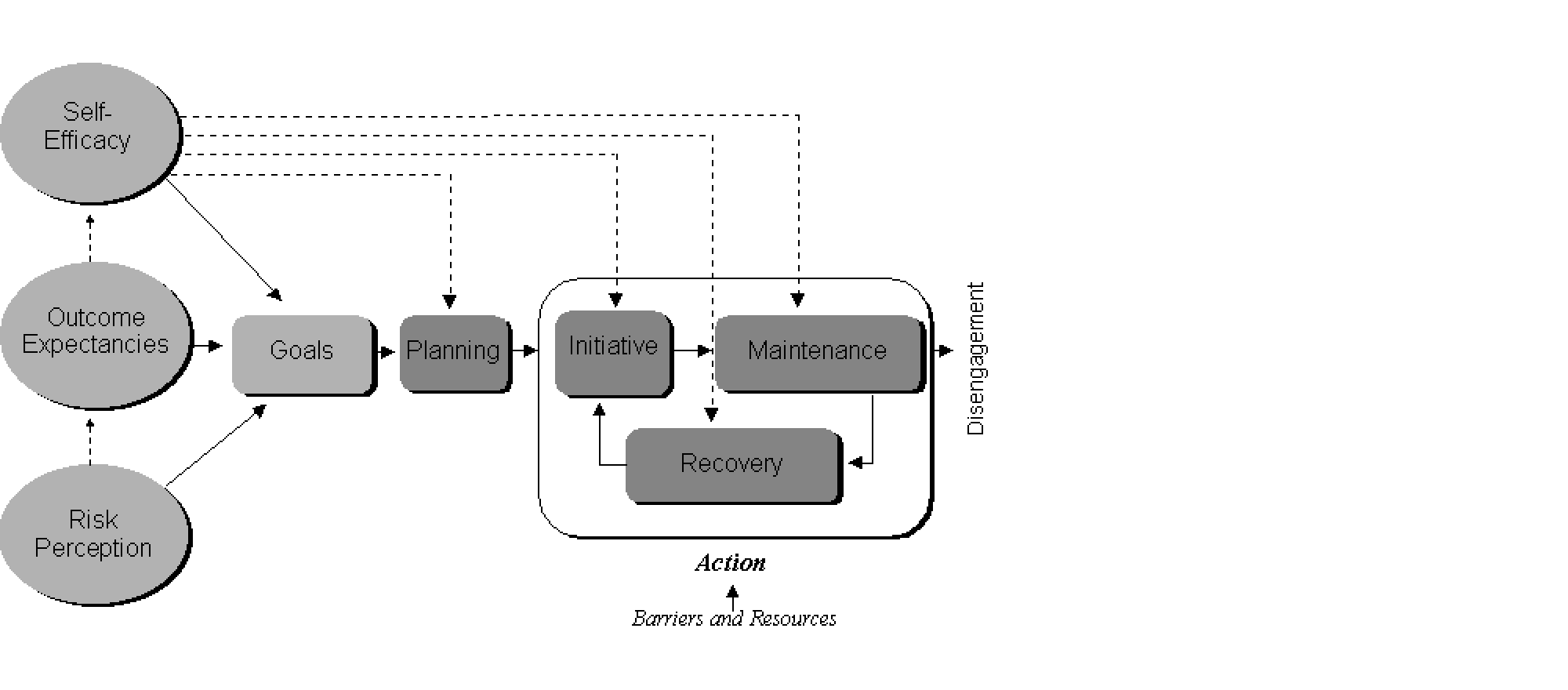
The model suggest that a person's intention to perform a behavior is influenced by their perceptions of risk, their expectations about outcomes, and their self-efficacy. Intention mediates the person's planning of action and coping (i.e. planning around potential setbacks), and these in turn influence the behavior.
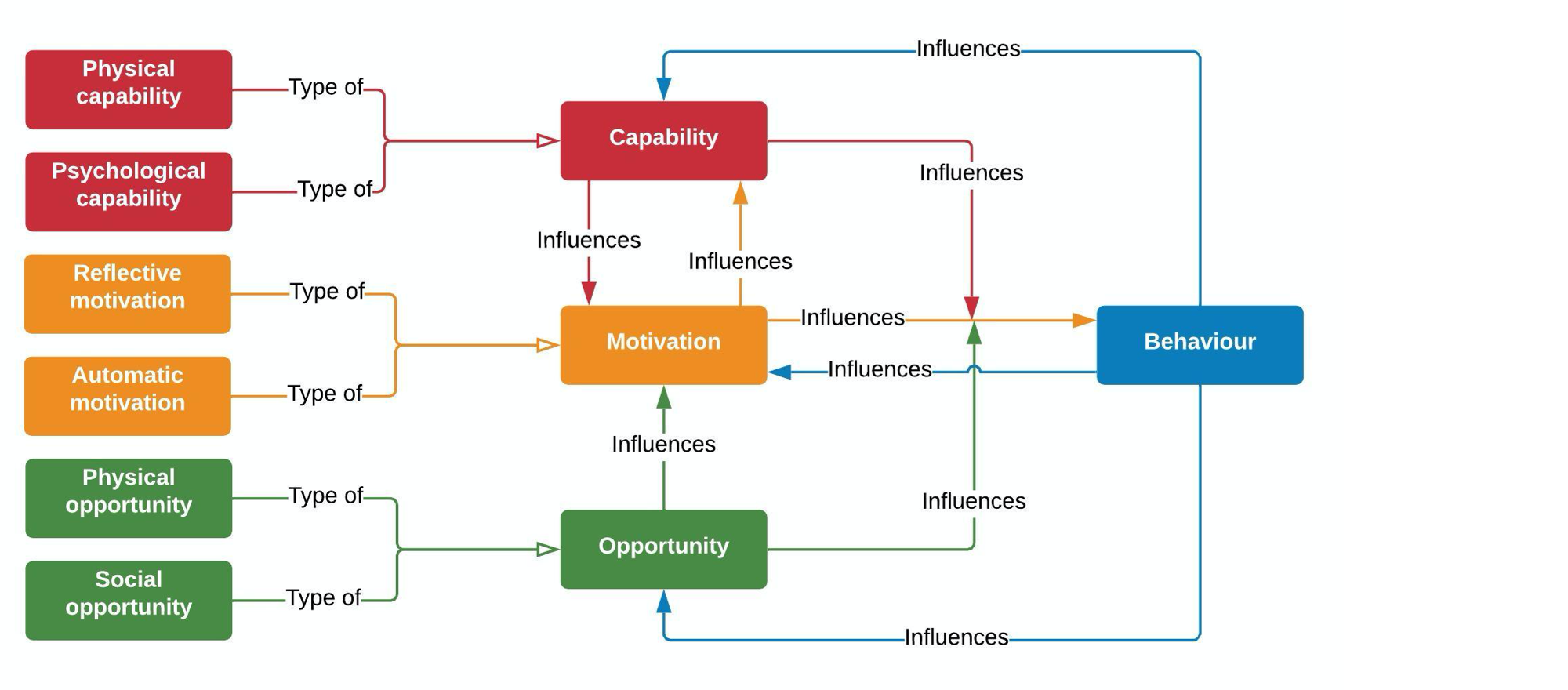
Social support, environmental factors, and other influences play a role at all steps.
HAPA is noteworthy in distinguishing self-efficacy at the intitial performance, maintenance stage, and recovery (i.e. failure) stages of the behavior. For example, a person may believe they can do a behavior initially but not necessarily believe they can stick with it for the long-term, and this may influence their plan of action.