Learn how to change behavior.
The world's largest collection of resources and data on behavioral science.
Behavior change and behavior design models
MODELS
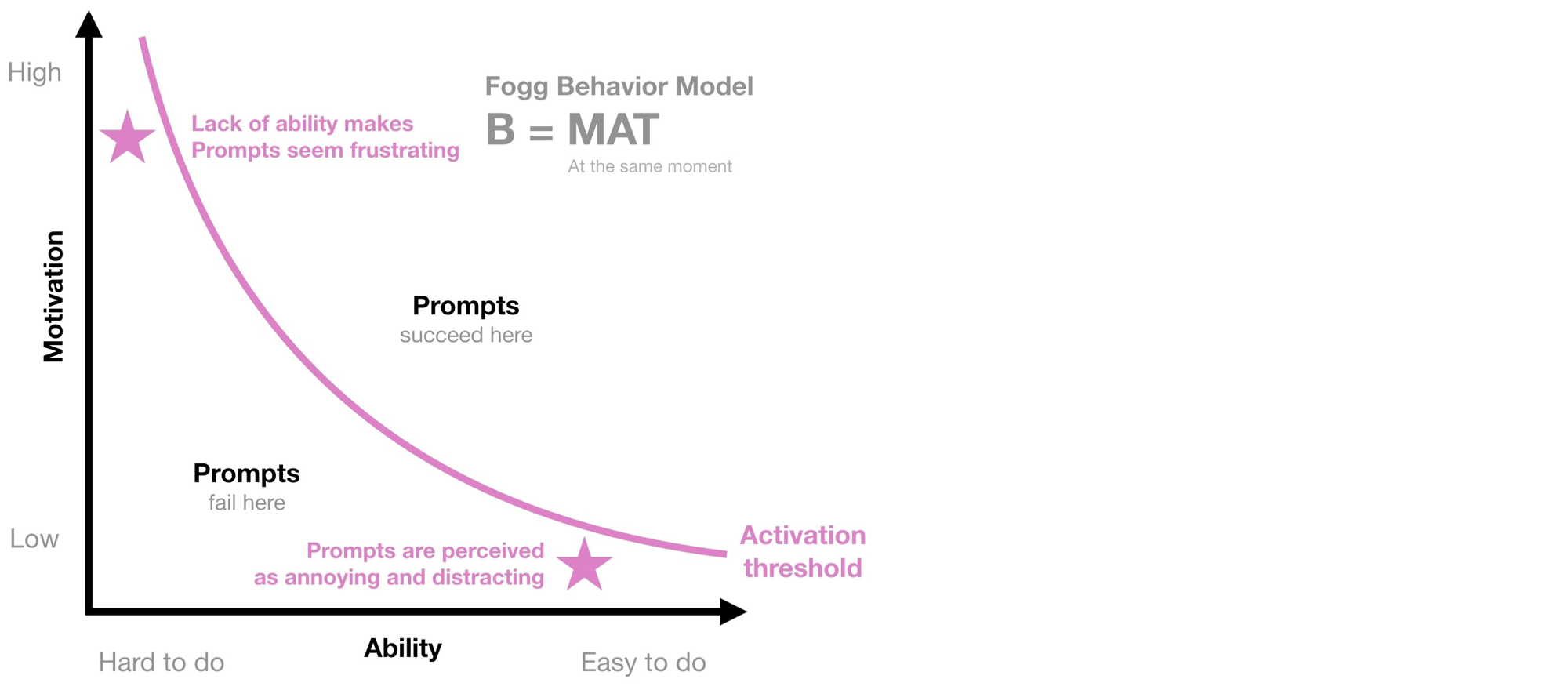
Fogg Behavior Model
TYPE
Behavior model
PEOPLE
BJ Fogg
MODELS
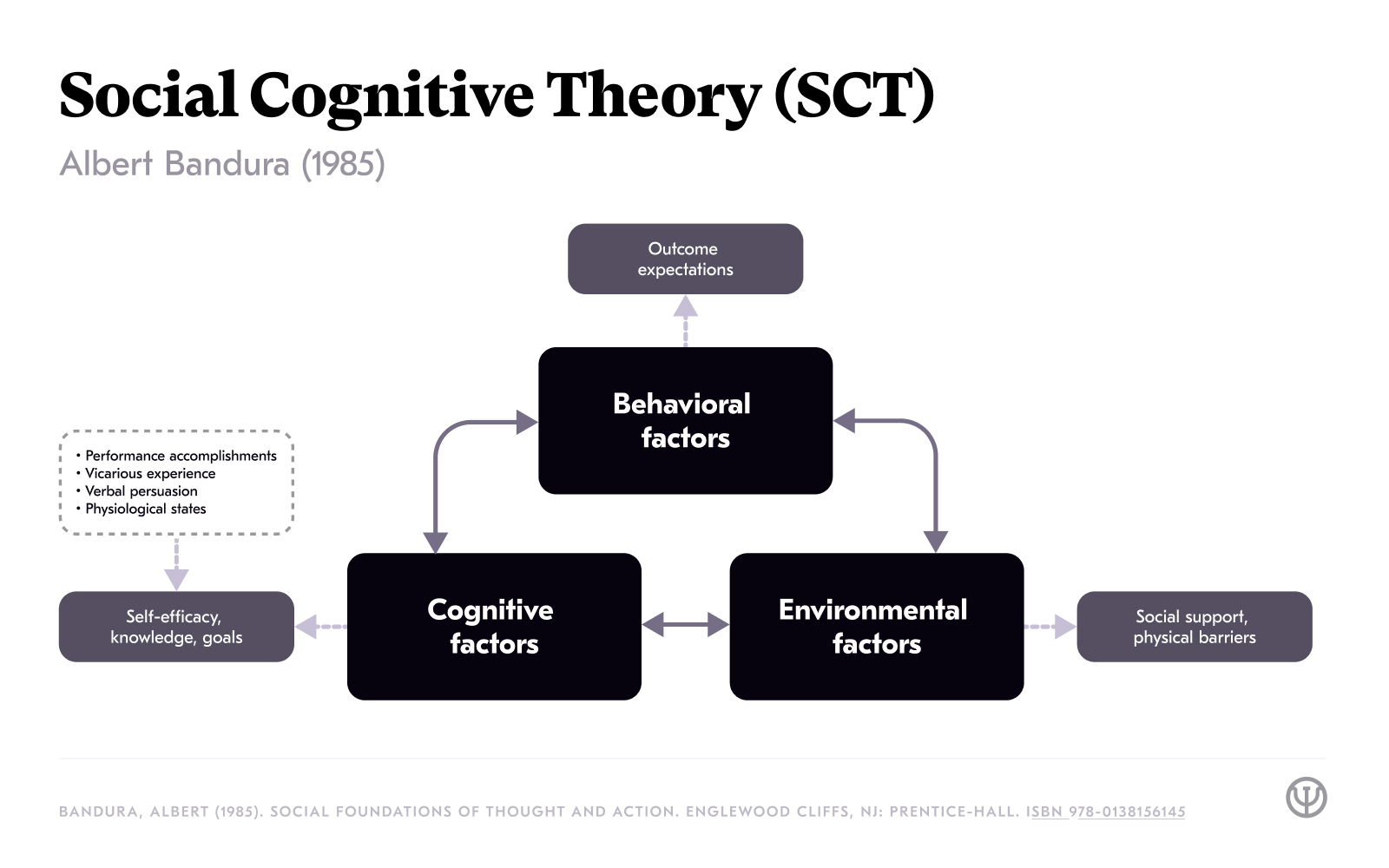
Social Cognitive Theory
TYPE
Behavior model
PEOPLE
Albert Bandura
MODELS
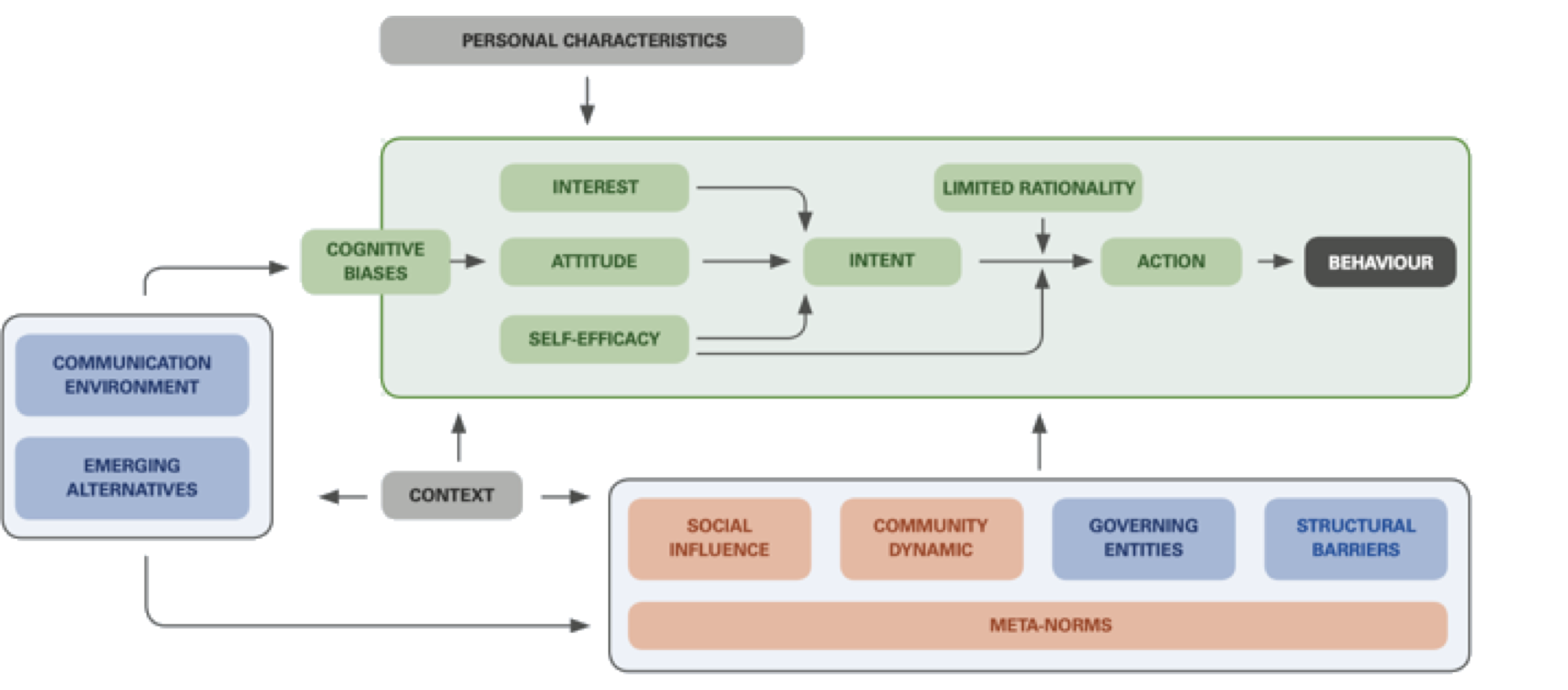
Behavioural Drivers Model
TYPE
Behavior model
PEOPLE
Vincent Petit
ORGANIZATION
UNICEF
MODELS
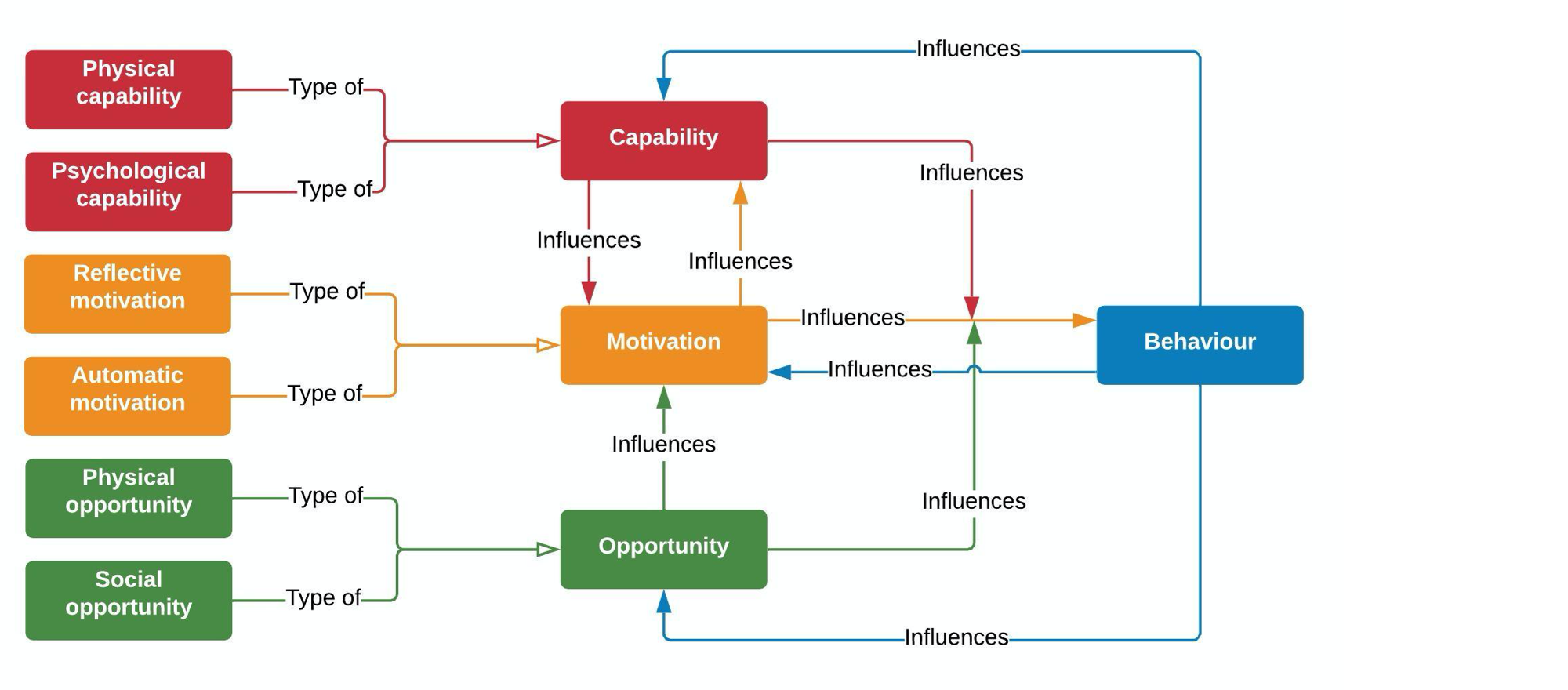
COM-B | Capability, Oppportunity, Motivation → Behavior
TYPE
Behavior model
PEOPLE
Susan Michie, Robert West, Maartje van Stralen
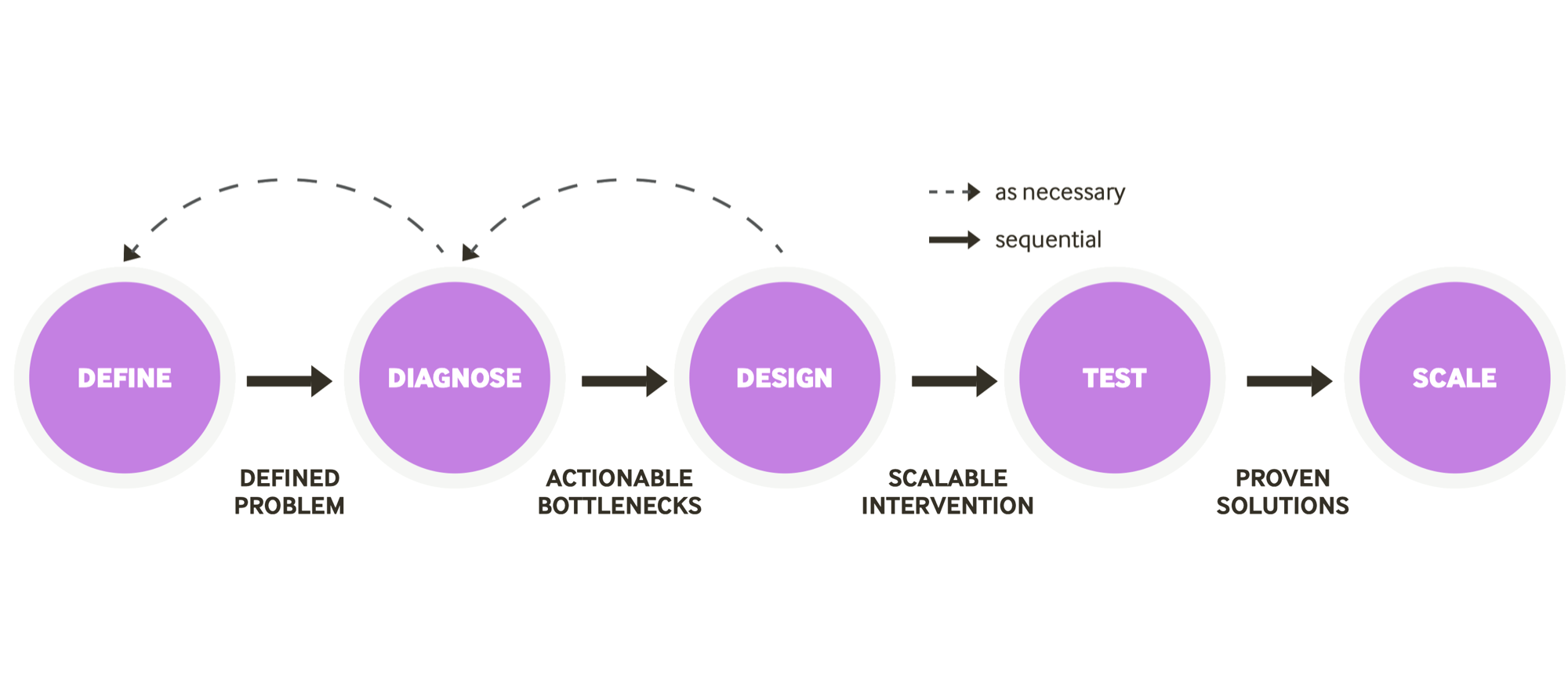
MODELS
Behavioral Design Process
TYPE
Behavior design process / heuristics
PEOPLE
Anthony Barrows, Natalie Dabney, Jon Hayes, Rachel Rosenberg
ORGANIZATION
ideas42
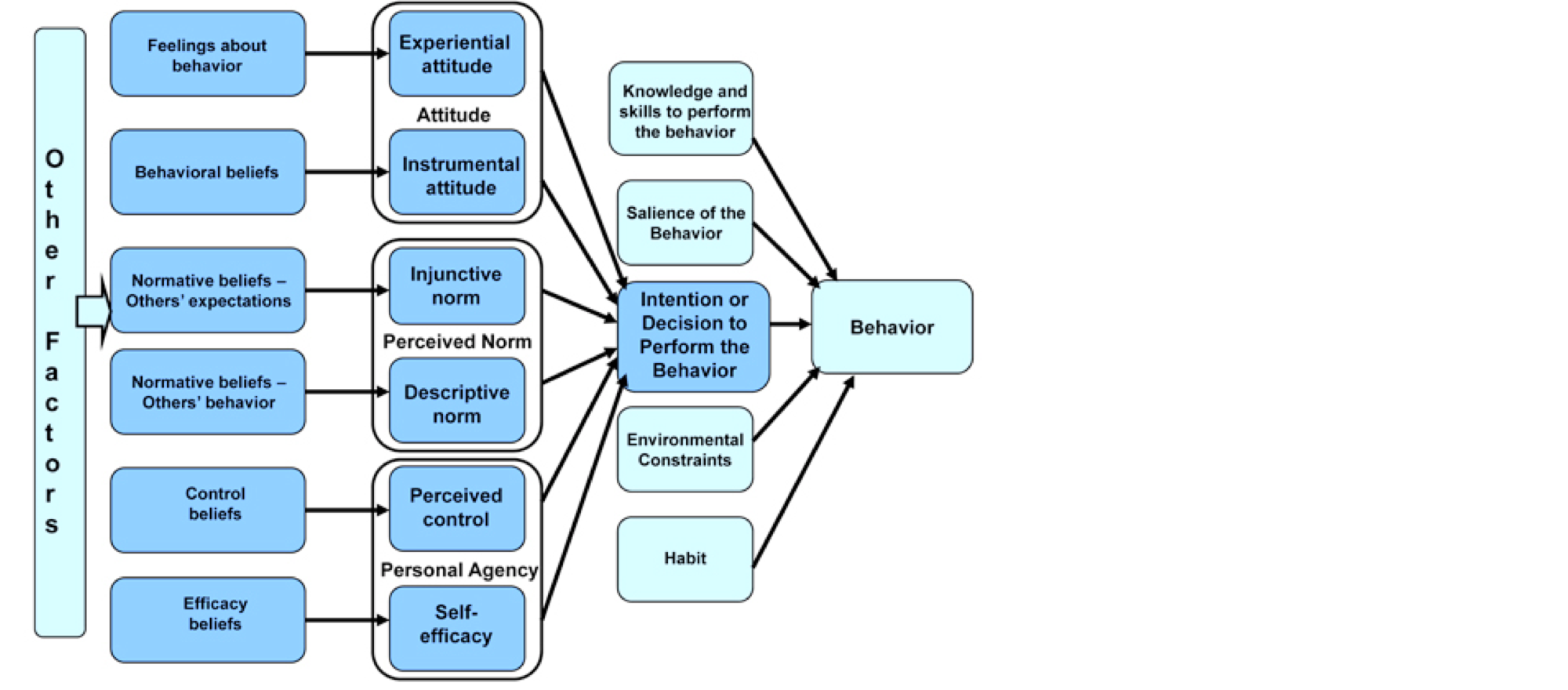
MODELS
Integrated Behavior Model
TYPE
Behavior model
PEOPLE
Martin Fishbein, Icek Ajzen
Tactics that change behavior

TACTICS
Behavior Substitution
Behavior substitution refers to attempting to eliminate a problematic behavior by replacing it with another one. Often, the substituted behaviors are intended to have similar sensory qualities (e.g. drink flavored sparkling water instead of soda). The goal is typically to disassociate the original behavior from its cue, enabling the more positive behavior to be triggered automatically.

TACTICS
Depression rating
Depression rating simply refers to having someone rate their mood. Often, this may be an informal method like a smiley-face based Lickert scale or choosing a word from a list, rather than using a standardized instrument like the Beck Depression Inventory.

TACTICS
Automation
Automation refers to having another person, group, or technology system perform part or all of the intended behavior. A prominent example is Thaler & Bernartzi's Save More Tomorrow intervention, which invested a portion of employees' earnings into retirement funds automatically and even increased the contribution level to scale with pay raises. Other examples include automatically scheduling medical appointments so the patient needn't do it themselves and mailing healthy recipe ingredients to the person's home to reduce the burden of shopping.

TACTICS
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a therapuetic approach to improving mental and behavioral health. The core philosophy is that behavior can be modified by noticing and correcting patterns in thought that influence the behavior. Modern CBT is typically associated with Albert Ellis and Alan Beck.The structured and rules-based nature of CBT have made it a popular candidate for digital interventions and application by lightly-trained or even untrained practitioners.

TACTICS
Education or Information
Education refers to empowering a person with more knowledge or training than they had previously. While providing information alone is often a suboptimal way to drive meaningful behavior change or long-term interventions, the right message at the right time can be a powerful part of a behavior change strategy.

TACTICS
Checklists
Checklists are an age-old tactic for remembering to do certain tasks. Checklists are sometimes used to measure behaviors that should take place with a certain frequency, e.g. every day or X times per week, and other times, to ensure certain steps are followed every time a person does a complex behavior.For behavior designers, the challenges of checklists often entail choosing the right behaviors, breaking them down to the correct level of granularity for a given population, and serving them up in the proper context or sometimes with personalization. They are likely underutilized and consistently improve the performance of even experts, like pilots and surgeons.

TACTICS
Covert Learning
Covert learning refers to imparting educational information into non-traditional methods of delivery. For example, a film where someone learns cognitive behavioral therapy techniques or receives training on body-weight fitness exercises may teach someone how to do these (or at least generally what they are). People may also learn the consequences of a behavior through watching someone else experience them, and this concept (viarious experience) is a key component of Bandura's social cognitive theory.

TACTICS
Clawback Incentives
Clawback incentives refer to a framing effect applied to rewards where participants are intended to experience losing the reward via noncompliance rather than accruing it for successful performance of the behavior.For example, a hypertension management program may credit its participants $200 at the beginning of the month, and reduce or "claw back" the amount by $3 each time the patient does not take their medication. The alternative would be starting the month at zero or the previous ballance and adding $3 each time the patient takes the medication.
Products that change behavior

PRODUCTS
Advanced Brain Monitoring

PRODUCTS
10% Happier
Behaviors
Mental Health & Self-Care
Tactics
Reminders, Cues, & Triggers +5 more

PRODUCTS
AdhereTech

PRODUCTS
AbleTo
Behaviors
Mental Health & Self-Care
Tactics
Personalization, Skill Coaching, Coaching or Counselling

PRODUCTS
Accion
PRODUCTS
2Morrow Smoking Cessation Program
Behaviors
Smoking Cessation
Tactics
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Behavioral Activation (BA)
Models
ACT

PRODUCTS
APDS
Behaviors
Crime
Tactics
Social Support, Reminders, Cues +5 more
PRODUCTS
2Morrow Chronic Pain Program
Behaviors
Mental Health & Self-Care, Other, Disease Management
Tactics
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Behavioral Activation (BA)
Models
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Research on behavior change
PAPERS
The PULSE (Prevention Using LifeStyle Education) trial protocol: a randomised controlled trial of a Type 2 Diabetes Prevention programme for men.
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity, Diet & Nutrition
PAPERS
Physical activity with spiritual strategies intervention: a cluster randomized trial with older African American women.
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity
TACTICS
Spirituality
PAPERS
The program for rheumatic independent self-management: a pilot evaluation.
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity
PAPERS
A Digital Diabetes Prevention Program (Transform) for Adults With Prediabetes: Secondary Analysis
PRODUCT
Transform
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity, Diet & Nutrition
PAPERS
Nutrition education worksite intervention for university staff: application of the health belief model.
BEHAVIOR
Diet & Nutrition
PAPERS
Continuous glucose monitoring counseling improves physical activity behaviors of individuals with type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial.
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity, Disease Management
PAPERS
Value-Based Insurance Design Improves Medication Adherence Without An Increase In Total Health Care Spending
PAPERS
The Effectiveness of Prompts to Promote Engagement With Digital Interventions: A Systematic Review.
BEHAVIOR
Other
PAPERS
The effects of a multimodal intervention trial to promote lifestyle factors associated with the prevention of cardiovascular disease in menopausal and postmenopausal Australian women.
BEHAVIOR
Physical Activity